AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor: Overview
This topic explains how to apply an AC voltage to a resistor and find the value of the current using Kirchhoff’s loop rule. It also discusses the root mean square or effective current and voltage with its value, formula and notation.
Important Questions on AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
A capacitor is connected to source. The capacitive reactance and the RMS current would be:
An a.c. source, of voltage , is applied across a series LCR circuit. Which of the following is the phasor diagram for the circuit when capacitative impedance exceeds the inductive impedance?
A resistor of and a capacitor of 15.0 are connected in series to a 220 V, 50 Hz a.c. source. Calculate
(i) The current in the circuit.
(ii) The rms voltage across the resistor and the capacitor.
The instantaneous current and voltage of an a.c. circuit are given by and . What is the power dissipation in the circuit?
In a series LCR circuit, the voltage across an inductor, capacitor and resistor are , and respectively. What is the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit?
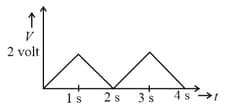
The RMS value of voltage of the waveform shown below is, , find the value of .
Chose the correct phasor diagram for a purely resistive a.c. circuit.
The graph between the current in a purely resistive a.c circuit and the alternating voltage applied is a_____.
Which graph represents the true resistive a.c. circuit?
Discuss a purely resistive circuit.
If a capacitor of is connected to a , AC source and the current passing through it is then the rms voltage across it is
Assertion : The alternating current lags behind the e.m.f. by a phase angle of , when AC flows through an inductor.
Reason : The inductive reactance increases as the frequency of AC source decreases.
Assertion: In a purely resistive ac circuit instantaneous power varies sinusoidally.
Reason: Applied ac voltage varies sinusoidally.
A sinusoidal voltage is applied to a resistor of resistance. Calculate the power dissipated as heat in .
A sinusoidal voltage is applied to a resistor of resistance. Calculate the frequency of the supply.
The r-m-s value of AC voltage in terms of and is always same for a complete cycle.
The r-m-s value of and is _____ times for a complete cycle. Here, is peak voltage.
Compare the r-m-s value of and for a complete cycle. Here, is peak voltage.
The average value of for the interval is _____.
Find the average of the given function for the interval to .
